Posts
SEO Basics 4 - Technical SEO

This is the fourth and final post in a series about the basics of search engine optimization. In this post, we cover technical optimizations from sitemaps to page speed.
Nicholas Molina
March 5, 2020
Technical Key Signals
Essentially all optimizations that aren’t content or link based fall under the category of Technical SEO. Technical SEO used to be mostly about helping bots crawl and index websites, but its definition has expanded as search engines became more sophisticated. Modern Technical SEO includes everything from page speed to structured data. In this final post, we’ll briefly review the major categories of Technical SEO.
Optimizing for Bot Crawling and Indexing
Getting large sites indexed with Sitemaps.xml
As mentioned in our first article, search engines gather information using bots that crawl websites and log their information into the search index. Bots discover new pages to crawl using links between websites or through a website’s sitemap, which is stored in a special file called sitemap.xml.
The sitemap.xml file lists all the pages of a website in a bot friendly format that helps bots find, understand, and index your site. You can create your sitemap using the website xml-sitemaps.com, or if you’re using Wordpress, the Yoast SEO Plugin. Once your sitemap is generated, you can submit it for crawling using Google’s or Bing’s webmaster tools.
Excluding content from indexing with noindex and Robots.txt
You may want to exclude content or even whole directories from search engines. For example, you may want to exclude a form confirmation page from the SERP. To request content be excluded from the SERP, you can either add HTML to an individual page or use a special file called robots.txt.
-
HTML Noindex - To exclude individual webpages, add
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>in the page’s<head>. Then make sure any links to the excluded page are nofollow links. -
Robots.txt – For other content you can use the
robots.txtfile, which is basically a set of crawling instructions for search engine bots. Therobots.txtfile gets into advanced SEO concepts that are out of scope of this series and configuring it incorrectly can do some serious harm. It’s unlikely you’ll have a valid use case for editing arobots.txtfile. But, in case you do, here is a good summary if you’d like to learn more.
It is important to note, both noindex and robots.txt are merely requests. Most reputable search engine bots will follow your instructions, but other bots may not. You also can’t rely on reputable bots either as the rules are always changing. For example, as of September 2019, Google will ignore robots.txt noindex requests for HTML but not for other content, like PDFs or images. To be safe, never rely on noindex or robots.txt to keep content private. Don’t confuse obscurity for security - if you have sensitive content, don’t make it publicly accessible.
Page Speed, Security, and Usability
Why do search engines care about your website’s speed, security, and usability? Because they’re recommending their users to your site and if their users have a bad experience, it reflects poorly on the search engine. Again, the primary benefit search engines are providing is an answer – that answer is your website. Help them improve their user’s answer experience and they’ll reward you for it. Think of these enhancements as a win-win; you’re improving your website’s user experience and getting an SEO bump at the same time.
Optimize for speed
The faster your website loads, the faster the search engine’s user gets their answer. Thankfully, you can check your websites performance and learn what you can do to make it faster by typing the URL into any of these three websites: GTmetrix, pingdom, or Google PageSpeed Insights.
For obvious reasons, the one you want to pay the most attention to is PageSpeed by Google. But, before you go crazy trying to get a perfect 100, realize even many of Google’s own websites don’t get close to a perfect score. In other words, take the scores as a guide, not as the last word. Let me say it again, it’s OK if you don’t get a perfect 100. Aim for at least a 75 and make improvements where you can.
Some easy fixes to improve your score are minification, which works by shrinking file size, and caching, which works by temporarily storing files in the browser to reduce server requests. If you’re a Wordpress user, there are plenty of free caching and minification plugins for you to choose from. You can also try Cloudflare, a DNS provider that offers minification, caching, and various other services on their free plan.
Secure your site with HTTPS
Search engines don’t want to refer their users to websites where they could be vulnerable. Arguably, not every website needs to be encrypted with HTTPS, the greatest concern is with ecommerce sites where man in the middle attacks could steal payment information. But there are risks with other websites, if you have a conversion form, you want to make your users comfortable that their information won’t be hijacked.
Adding the S in HTTPS is surprisingly simple – and free – if you have a decent webhost that supports Let’s Encrypt. A free non-profit initiative to encrypt the web, Let’s Encrypt is easily configured in your webhost’s cPanel (if you use that sort of thing). Cloudflare also provides a free HTTPS service (as does Google Firebase, which is great for static site generators, like Hugo).
Whichever method you use, make sure to redirect all of your old HTTP content to the new HTTPS version, otherwise you’ll risk hurting your SEO ranking or triggering browser mixed content warnings. You can set up redirects in your webserver .htaccess file (or equivalent), but Cloudflare may provide the easiest solution with their HTTP to HTTPS toggle.
Mobile friendly design
50% of all web traffic is mobile and at least half of searches are from mobile devices. If your website breaks on mobile, it can’t answer the user’s query and the search engine has failed to perform its core function. Wordpress and most WYSIWYG website builders offer responsive design features out of the box, meaning your site should automatically scale itself to the proper size at different reslutions. Unfortunately should and does are two different things, when making design changes, always test them out using a simulator like Device Mode in Chrome’s DevTools. If you want to make sure your site is mobile friendly, try using Google’s Mobile Friendly Test.
Search Result Presentation
SEO isn’t all about rank, it’s also about presentation. It’s important not to forget there is always a human on the other end of the SERP. Not only does your webpage need to rank highly, its search result needs to answer the question the user – a human – was asking. If not, they won’t click, and your rank efforts were all for nothing.
Attract Visitors with Pretty URLs
While keywords in a URL has fairly little effect on SEO rank, URLs represents one third of a search result’s content (the other thirds being page title and description). User’s like clicking Pretty URLs or URLs they can understand at a glance. Let’s compare:
The first URL contains no usable information and is less likely to earn traffic from users trained to avoid suspicious looking links. The second, pretty URL is clearly about sectional couches. If I was looking for a sectional, I know what I’d click first. How about you?
More than eye candy, Pretty URLs reflect good site structure and a logical content hierarchy. Site structure is essentially how you’re organizing your content, be it in an actual folder hierarchy or virtually using a CMS, like Wordpress. In either case, your URL and site structure should make sense to your users. If it does, they’ll be more likely to visit, easier for them to find what they’re looking for, and ultimately make a purchase.
Pretty URLs are also helpful in link building. Everyone knows users find hyperlinks of random characters suspicious and are hesitant to share Ugly URLs or place on their site. Make it easier for others to link to you with a Pretty URL.
Enrich your search results with structured data
A more powerful way to improve search result appearance is with structured data. Structured data is basically extra information that helps Google better understand your content. With that better understanding, Google can use rich results or rich snippets to display your search result in a more meaningful and prominent way. Some of the most common rich result features include reviews, ratings, product overviews, and logos. Google maintains a gallery of the available rich results.
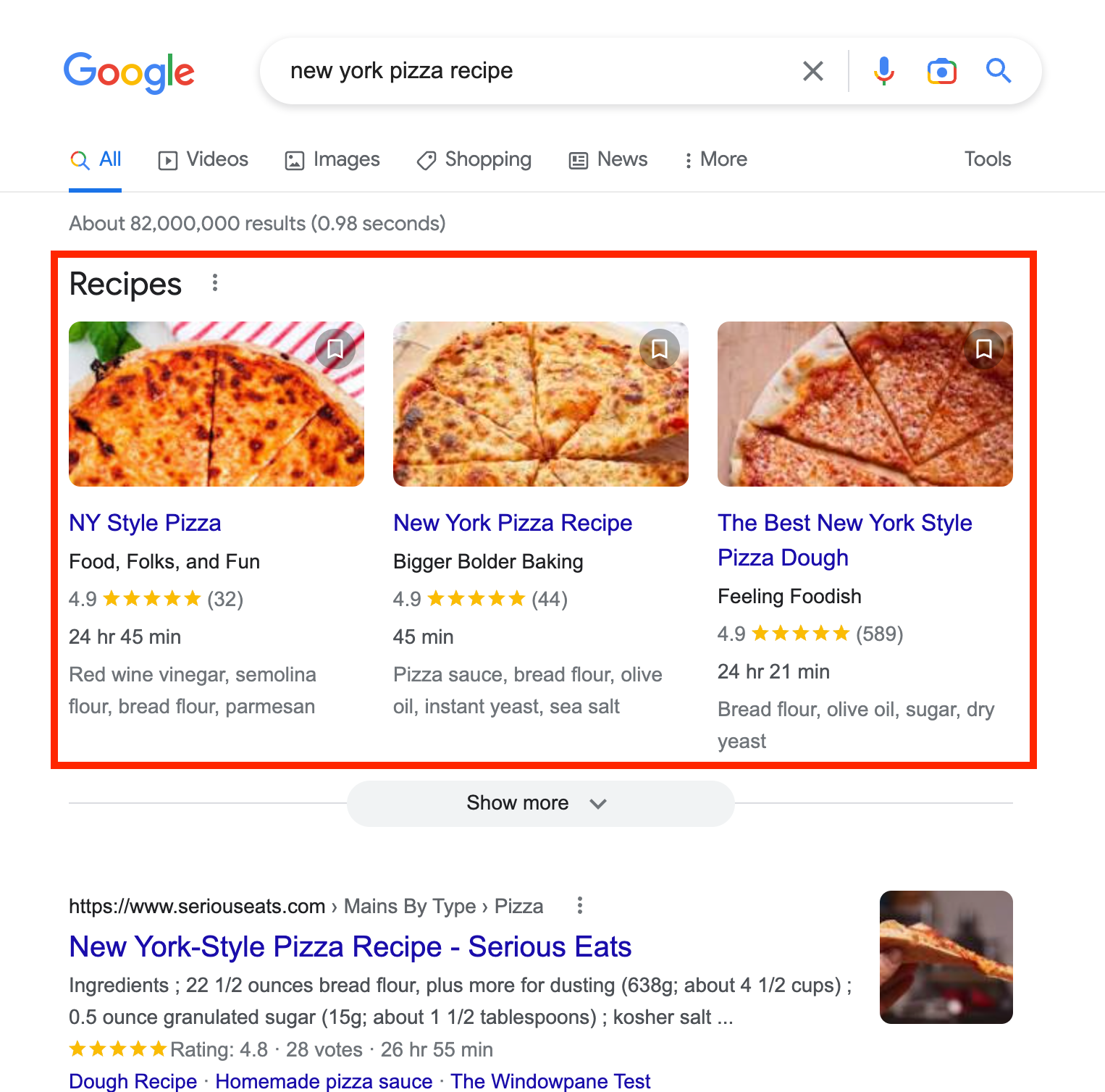
The code required to deploy structured data may look intimidating but really boils down to data tagging. If you’re using Wordpress, the Yoast SEO Plugin will generate most structured data for you, which you can then check for yourself using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
Knowledge Panel and Google My Business
While we’re here it’s worth mentioning knowledge panels and how you can get your business in it. Knowledge panels are like super rich search results that are prominently displayed in a special area (usually a side bar) of the SERP and provide a snapshot of the search subject.
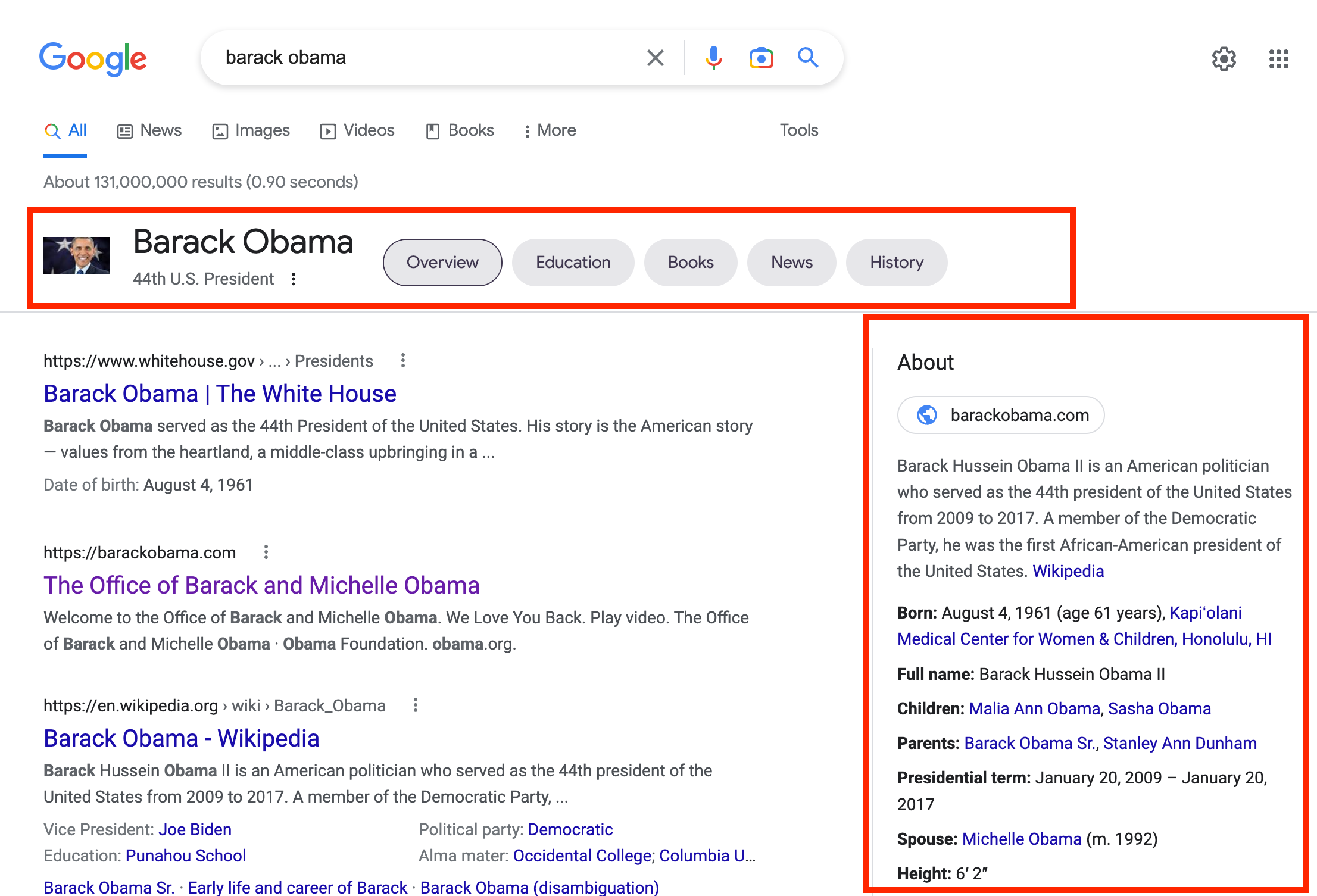
Thankfully, it’s easy to get your business listed in a knowledge panel with a Google Business Profile from Google My Business. Google My Business provides you with a customizable profile that is likely to show up when users search for your company name. It also gets your business listed on Google Maps, which is huge — even crucial depending on what industry you’re in.
What we’ve learned
- Use sitemap.xml to get help your site get crawled, into the index, and onto the SERP.
- Use noindex and robots.text to exclude content from the SERP.
- A few actions that are good for your users and good for your search results:
- Make your site more secure with HTTPS.
- Make your site faster by following website best practices.
- Make your site mobile friendly with a responsive design.
- Attract users with better looking search results
- Have Pretty URLs and a logical site structure
- Enrich your search results with structured data
- Get your business listed in the knowledge panel and Google Maps with Google MyBusiness
Final Thoughts: It all comes back to content and usability
Search engines are focused on delighting their users by providing them the best answer as quickly as possible. Thankfully, your goals are aligned. Focus on delighting your users with great content and an excellent user experience and the search engines will reward you with higher ranking results and more visitors.
Free resources and tools
This series sought out to cover the basics of SEO quickly, yet thoroughly enough for a small business owner to get started. There’s a lot more to learn if you’d like to continue your journey. Below are some free resources and tools that can help you along.
-
Google Analytics – Track your website visitors, understand their behavior, and optimize for conversions.
-
Google Webmaster Tools – Monitor your site’s SEO health, including indexing and crawl status.
-
Google PageSpeed Insights – Check your website speed and mobile usability. Don’t obsess over this score!
-
Google Mobile Friendly Test – Check how mobile friendly your site is.
-
Yoast SEO – Wordpress plugin that auto generates structured data, sitemaps.xml, recommends best practices, and more.
-
Screaming Frog SEO Spider – An application that crawls your website to find broken links, errors, redirects, and more.
Other questions. Try Googling it!